Processes and Threads
Processes and Threads
- A process (aka task / job) is an instance of a program
- A thread is a unit of execution of a process

- PID
8498is the main process - PIDs
8499and8500are the threads
Process Control Block (PCB)
The Process Control Block is a data structure which holds the information related to a process.
- PID
- Registers
- Program Counter
- Stack Pointer
- Process State
- File Descriptors
- etc…
The kernel keeps track of all PCBs in a process table
Process Run State
A process can be in one of the following states
- RUNNING - Process is currently active
- READY - Process is inactive, but ready to run
- BLOCKED - Process is inactive, but not ready to run
A process that is in the READY state is often as a result of that process using up its allocated execution time
A process that is in the BLOCKED state is often as a result of the process waiting for some IO request
Threads
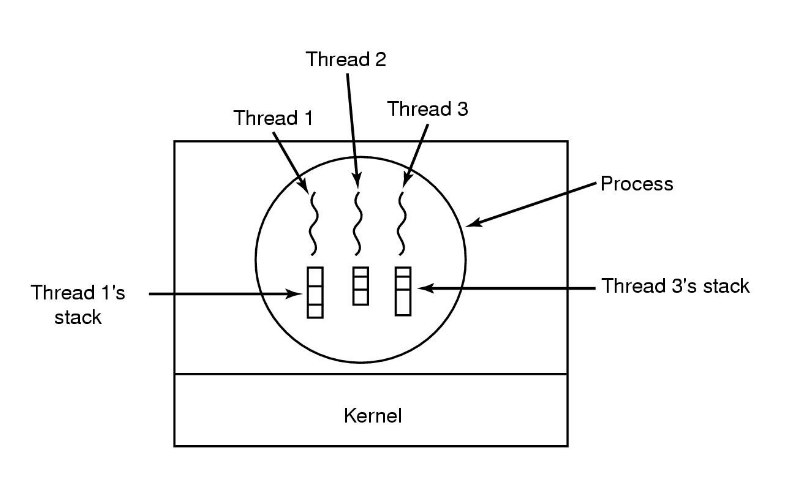
Threads
A unit of execution of a process
Each thread has its own stack, where local variables for that thread are stored. (The heap is shared between all threads of a process.)
Like how a process has a PCB, a thread has a Thread Control Block (TCB).
These contain thread-related data (i.e. thread program counter, registers, stack and state)
Kernel-Level Threads
Threads can be created by the kernel.
This gives the responsibility of managing threads to the operating system.
- Preemptive Multithreading
- Can pause the state of a thread
- Parallelism
- Can perform other tasks whilst one thread is blocked from an outstanding
syscall - Multiprocessor usage
User-Level Threads
Programs can also create self-managed threads.
This is useful in cases where custom thread management functionality is desired.
This is often however difficult to implement, and does not take advantage of the whole system
- Does not utilise multiple CPU cores
- A blocking
syscallwill block the entire process
Process vs Threads
Processes are independent of each other, and have their own dedicated memory and resource allocation.
Threads of a process share the allocated resources.
| Processes | Threads | |
|---|---|---|
| Memory | Independent | Shared |
| Resources | Independent | Shared |
| Crash | Independent | Shared |