Harms of Drug Use
Contents
Types of Harm
Medical
Organ damage
Neurotoxicity
Infections
Fetal exposure
Dependence
Injuries
Social
Relationships
Low education
Violence
Accidents
Criminality
Burden on health system
Economic
Poor occupational attainment
Financial hardship
Poverty
Cost to employers
Homelessness
Cost of healthcare
Burden of Disease
- Prevalence & exposure to substances
- Proportion of "problem users"
- Disease categories that are linked to use of the substance
Reporting Metrics
- Years lived in ill health or with disability (YLD) - Non-fatal burden
- Years of life lost (YLL) - Fatal burden
- Disability-adjusted life years (DALY) - YLD + YLL
Deaths
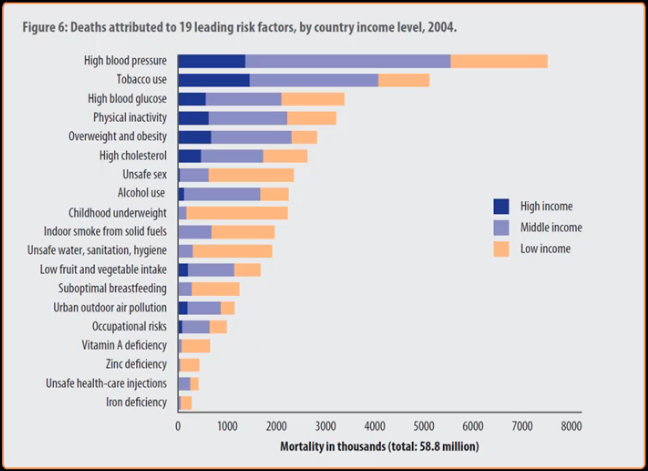
Note: #2 tobacco, #8 alcohol, illicit drugs omitted
DALYs
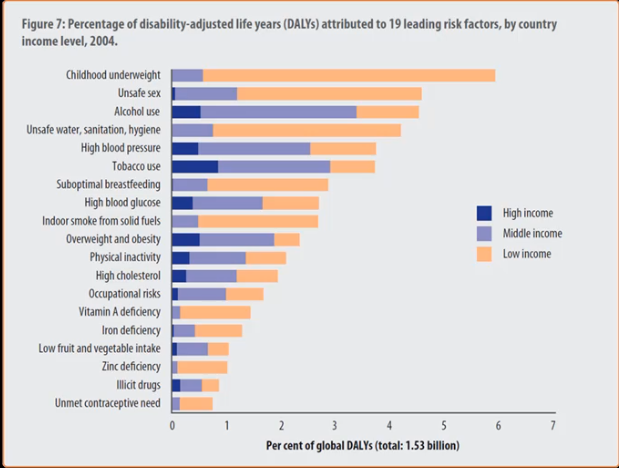
Note: #3 alcohol, #6 tobacco, #18 illicit drugs
Estimates
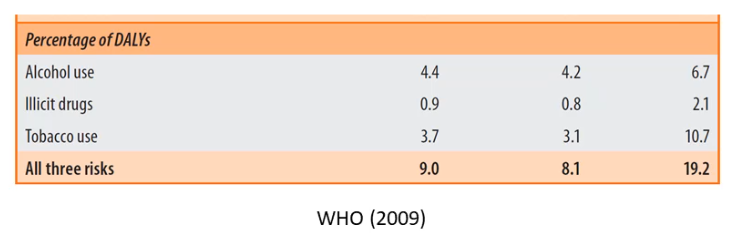
Tobacco, alcohol and illicit drug use was 15.9% of the proportion of DALY.
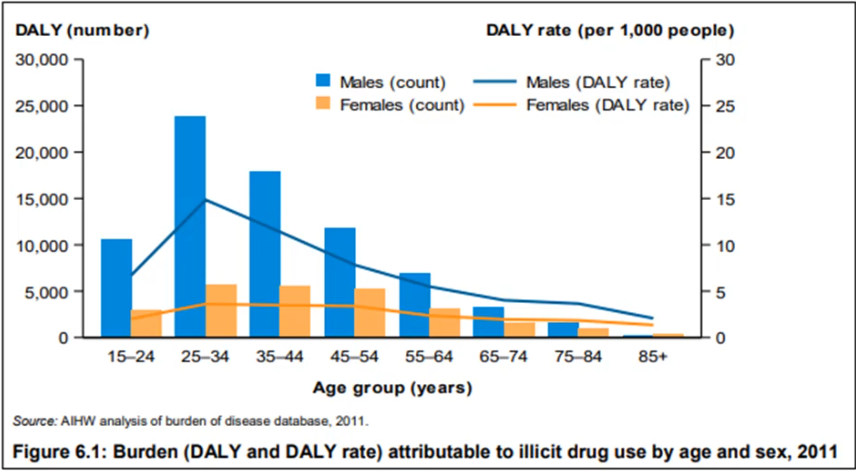
Burden of disease is greater in males (19%) compared to females (12.4%) - AIHW 2019
Tobacco, alcohol, illicit drug use
- 18% of deaths
- 21% male, 15% female
- 22% of YLL (fatal)
- 24% male, 19% female
- 10% YLD (non-fatal)
- 13% male, 7.7%
Tobacco
Leading risk factor to burden (9.3%)
13.3% deaths (20933)
~1.5x male prevalence
- 10.5% 2003
- 9.8% 2011
- 9.3% 2015
Alcohol
4.6% burden
3.4% deaths (5039)
~3x male prevalence
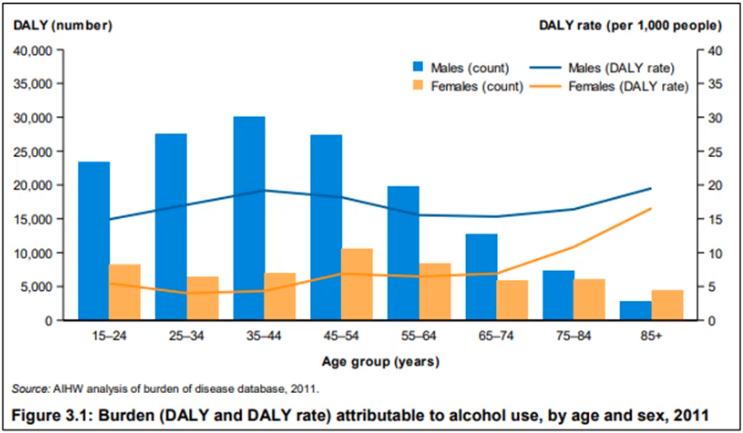
Higher in the younger age group 15-54
Highest 35-44
Illicit Drug Use
2.3% burden (101,865)
1.3% deaths (1937)
Harms To Users
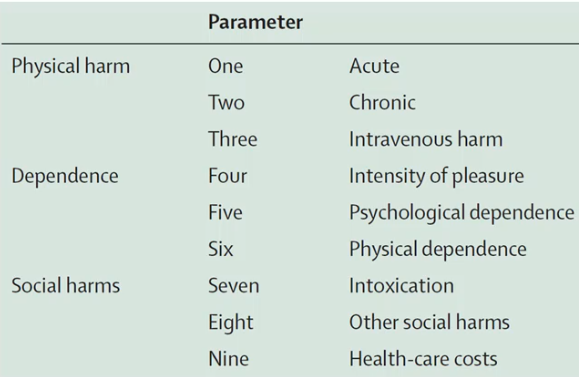
Each parameter has a 4 point scale (0 (no risk) - 3 (extreme risk))
Harm score = sum
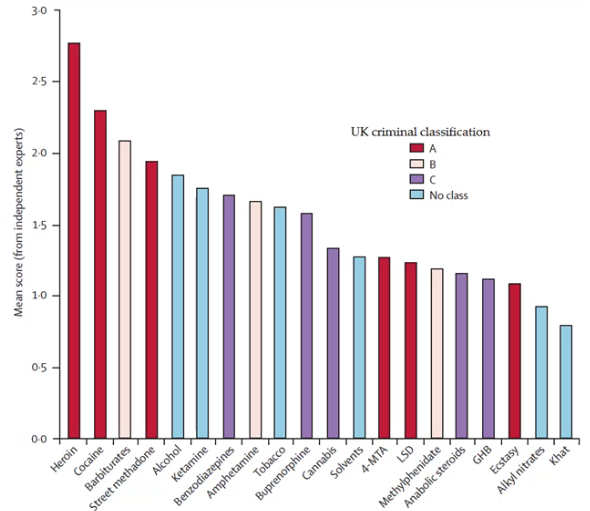
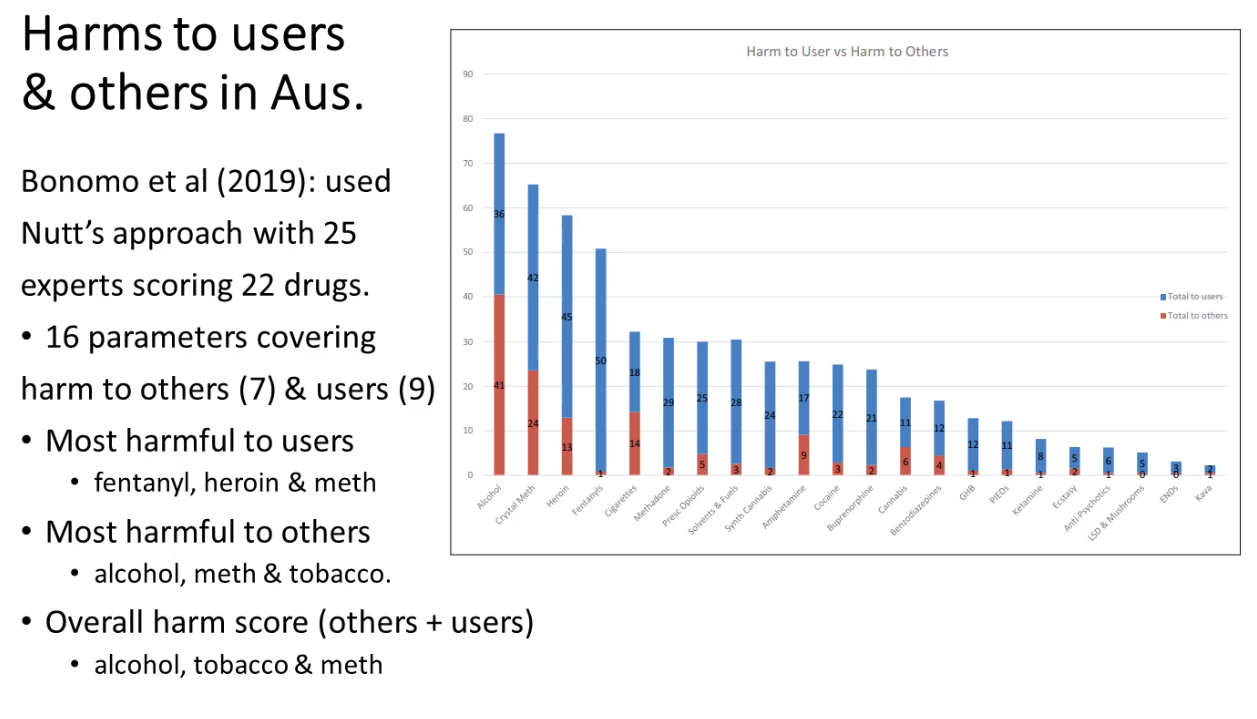
Alcohol was the most harmful drug to all
Drug use often starts in adolescence. Why?
- Drug use may cause poorer educational attainment
- or ... poor educational attainment may cause drug use
- or ... selling of drugs may be an attractive alternative to low paying jobs
- or ... a possible third variable (personality, illness, family, etc)
Occupational Success
Drug use is associated with greater occupational income in early adulthood (24-29), however it is also associated with reduced occupational income later on (29-35).
This may be as a result of early education exit (i.e. not going to uni so they can work).
- As income increases, drug use decreases
Neuropathology
Causes of neuropathic effects unclear.
- pyschoactive ingredient in the compound
- adulterants
- secondary illness
- infections/disease from consumption method
- accidents
Disclaimer: Associations are not causal
- grey matter - cell bodies
- white matter - fibres for neural communication
Nicotine
Brody et al. (2004) found that smoking is associated with decreased front matter volume in the frontal cortex.
He did an MRI scan and found decreased grey matter (cell bodies).
Note: This is only a scan for structural change. Functional change is not viewable
Heroin
Heroin is associated with a range of neuropathologies, that too decrease grey matter.
Cocaine
Associated with premature stroke, seizures, movement disorders (Buttner et al 2003)
Negative correlation between white matter integrity
Cannabis
Evidence of reduced metabolic activity
Reduced volume of the hippocampus and amygdala
Alcohol
Cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, liver stress
**Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
**
Reduction of the brain tissue
Inability to remember new things
Methamphetamine
Second most cause of strokes and hemorrhage in people < 45 years (Buttner 2011)
Dopamine activity recovers, however it recovers less with extended use
Harm Minimisation
Substance is is part of society. Harm minimisation is about reducing the harm to both the user, and to society.
Harm Reduction for injecting users
- Needle exchange programs - access to clean needles
- Reduces use of shared needles
- Reduces the amount of needle stick injuries
- Reduces transmission of HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis B & C
- Reduce health care costs
Harm Reduction for opioid users
Naloxone overdose kits
Naloxone - an injectable compound which blocks the effects of opioids and reverses overdose
