Thermal Conductivity
Tuesday, 29 May 2018
1:34 PM
Types of Heat Transfer
Conduction - direct transfer
Convection - mass motion of molecules
Radiation - Electromagnetism
Conduction
- Atoms/molecules/electrons gain energy, and collide with other particles, which also gain energy and collide
- This occurs when there is a temperature difference between particles.
- If - on a microscopic level - particles in different parts of an object have on average the same energy, then the net energy transfer is 0.
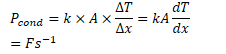
![]()
![]()
(Steady state - equal energy transfer rate into two states)
Compound slab
Convection
Bulk movement of a substance
- Natural convection, when the movement results from a difference in density
- Forced convection - Fan/pump/etc
Radiation
- All objects with a non-zero temperature emit energy continuously in the form of EM waves
- Dipole radiation //
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
Energy emitted per unit time by an object of temperature is![]()
![]()
-
power (W)![]()
-
Stefan's constant - ![]()
-
surface areaa![]()
-
emissivity (a ratio from 0 to 1)![]()
-
temperature (K)![]()
Emissivity
When , an object is considered a black body -
it is a perfect absorber and emitter of energy
When , and object is considered a white body
- it is a perfect reflector of energy
Kirchhoff's Law - a good absorber is a good emitter.
![]()
![]()
![]()