Contact Forces
Thursday, 8 March 2018
11:53 AM
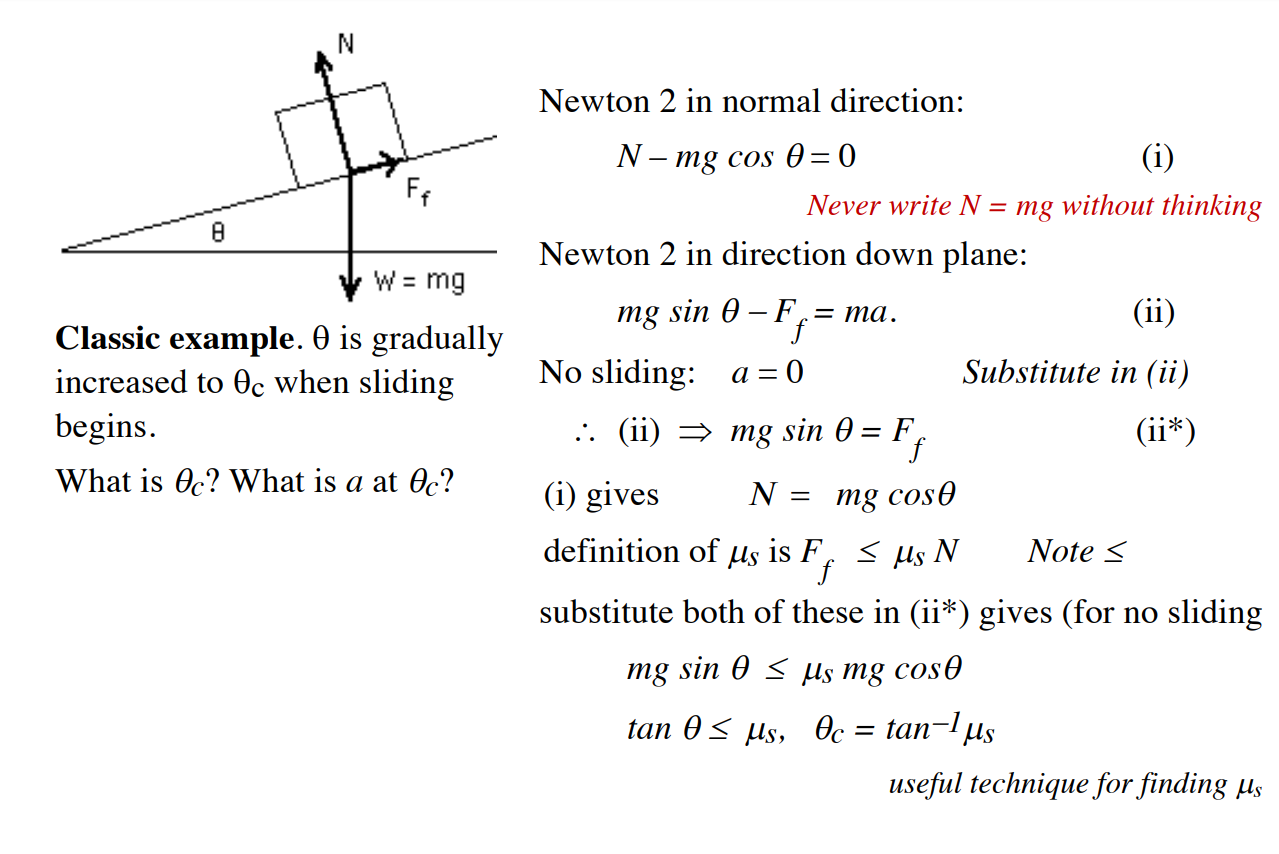
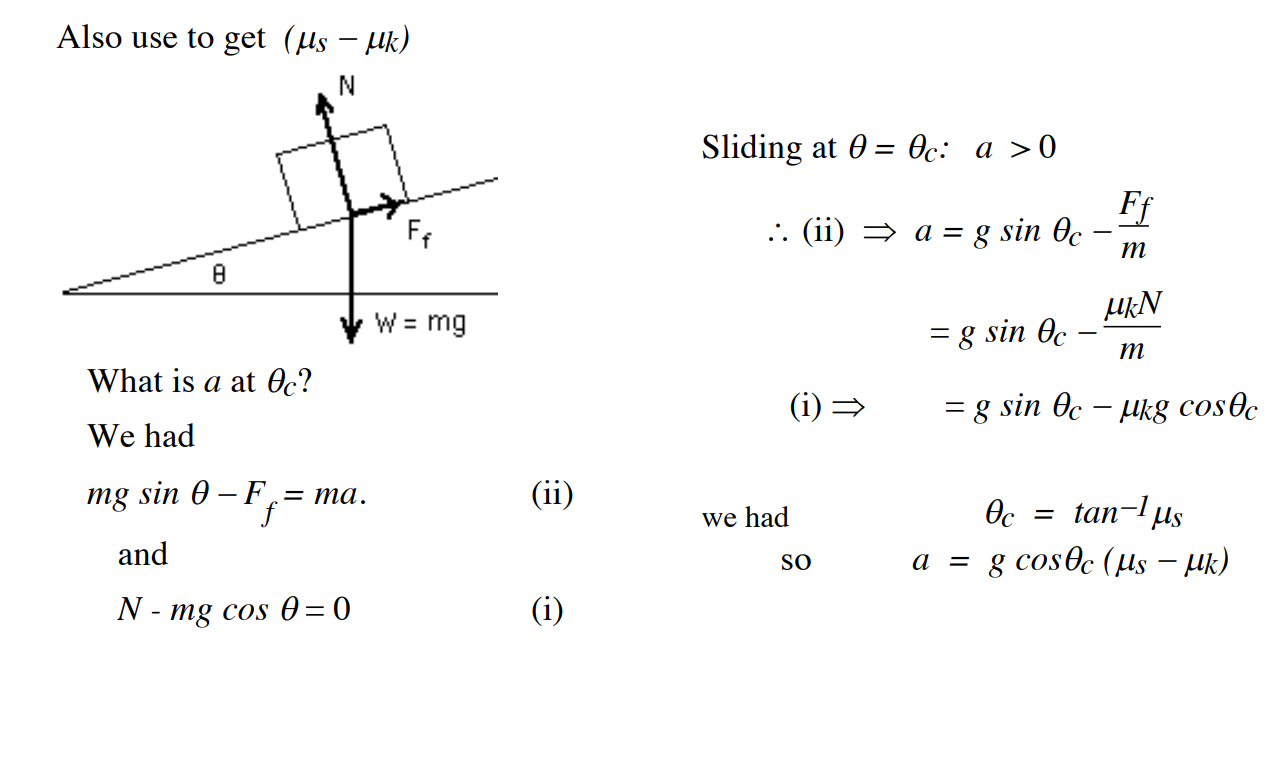
The normal component of a contact force is called the normal force N. The component in the plane of
contact is called the friction force . This division is arbitrary, but
useful.![]()
Normal force: at right angles to the surface
Friction force: in the plane of the surface
If there is relative motion, we call it kinetic friction, whose direction opposes the relative motion
If there is no relative motion, it is static friction, whose direction opposes the applied force
Kinetic friction (k)
![]()
Static friction (s)
![]()
is often less than (it takes less force to keep sliding than to
start sliding)![]()
Normal force
![]()
![]()