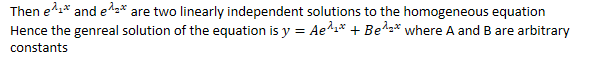Second Order Ordinary Differential Equations
Monday, 27 August 2018
10:34 AM
Theorem
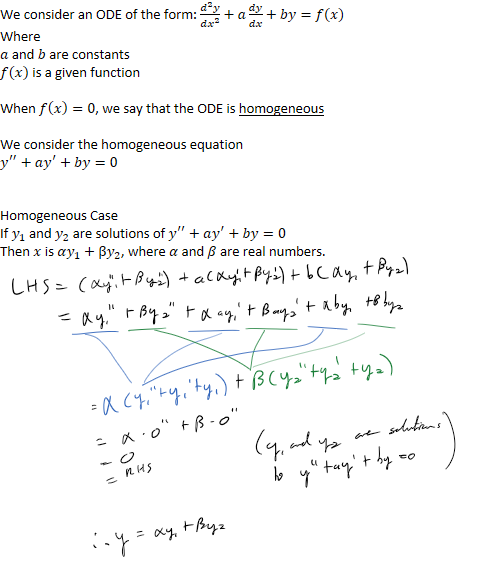
The homogeneous equation hsas two linearly independent solutions and
every solution is a linear combination of these solutions![]()
Notes:
- Two solutions and are linearly indepenent (they are not
constant multiples of each other)
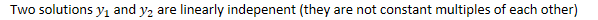
- If and are linearly independent solutions, then
every solution is of the form

Where and are constant![]()
Solving ![]()
Try a solution of the form ![]()
Then , ![]()
Substituting into the equation…
![]()
Since , then ![]()
satisfies the quadratic form - characteristic
(auxiliary) equation![]()
If then there are two real distinct roots![]()
Let and be the roots of the characteristic equation
and ![]()
Then and are two linearly independent solutions to the
homogeneous equation
Hence the genreal solution of the equation is where A and B are arbitrary constants