Capacitors
Monday, 20 August 2018
1:33 PM
A capacitor is a circuit element that stores energy in its electric field
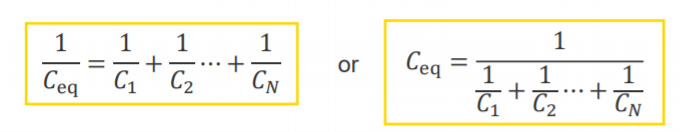
It consists of two conducting plates separated by an insulator (or a dielectric)
Usually, these
plates are aluminium foil
Dielectrics are often air, ceramic, paper, plastic or mica
When a voltage source is connected to the capacitor, the source
deposits a positive charge on one plate, and a negative charge on the other plate![]()
The charges will be equal in magnitude on both plates
The amount of charge is proportional to the voltage
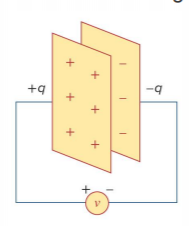
Capacitance is the ratio of voltage to charge across a capacitor, and is given the symbol ![]()
Capacitance is measured in farads , which is coulombs per volt.![]()
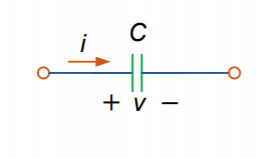
Capacitance depends on the physical dimensions and geometry of the capacitor.
For parallel-plate capacitors, the capacitance is given as
![]()
Where
-
Permittivity of the dielectric![]()
-
Surface area of each plate![]()
-
distance between the plates![]()
Capacitors are available in different values and types.
They are described by their dielectric material
They are usually rated in picofarads (), to microfarads ().![]()
They are used to block DC and pass AC signals, shift phase, store energy, suppress and filter noise, etc
Convention - Passive sign convention applies to capacitors as well
If , the capacitor is being charged
(absorbing energy)![]()
If , the capacitor is being discharged
(supplying energy)![]()
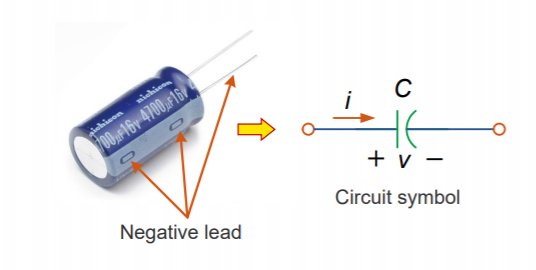
For capacitors in the range of particularly electrolytic ones, the polarity
is already assigned (on an electrolytic capacitor, the negative terminal is
physically marked)![]()
Equations
Charge = Capacitance x Voltage
![]()
Differentiation wrt time gives
![]()
Current is the rate of change of charge, so
![]()
Voltage is then
Where is called the intial voltage, or initial
conditions at time 
Instantaneous power delivered to the capacitor
![]()
The energy stored in the electric field that exists between the plates of the capacitor can be then calculated as
![]()
![]()
If , then ![]()
Properties
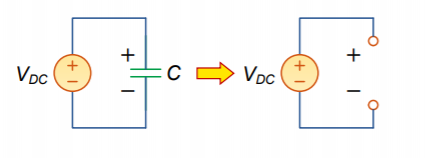
A capacitor is an open circuit to DC voltage.
This is because of the equation, ![]()
At a constant voltage, there is no change in voltage, and ![]()
Therefore, ![]()
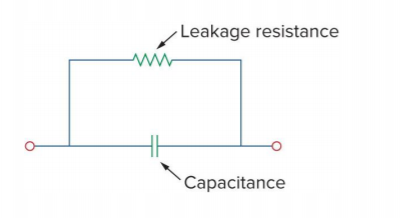
An ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy, energy is absorbed from a circuit, stored in an electric field, and then released back into the circuit
However, a real capacitor has a parallel-model leakage resistance, leading to a slow loss of the stored internal energy
Capacitors in Parallel
Capacitors can be added in series or parallel
For capacitors in parallel, the voltage is the same across each capacitor
Applying KCL and current-voltage relation for capacitors![]()

Capacitors in Series
Current is the same through each capacitor