Thevenin's Theorem
Monday, 20 August 2018
12:46 PM
The load of a circuit is an element that varies in its power usage
Every time the load changes, the circuit would have to be analysed again
Thevenin's theorem provides a technique to simplify the analysis by replacing the fixed part of the circuit with an equivalent one known as Thevenin equivalent circuit
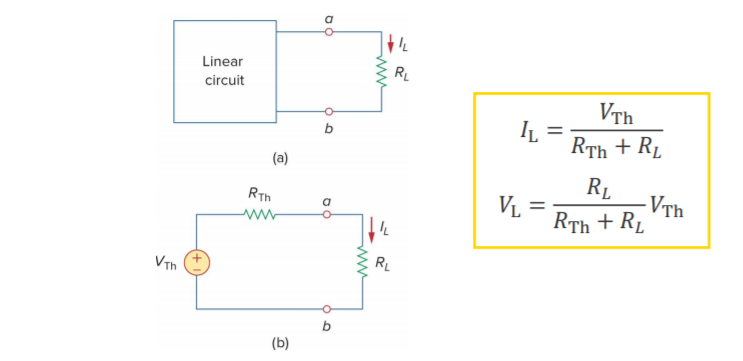
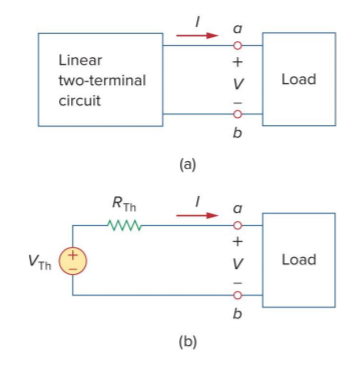
Thevenin's theorem - A linear two-terminal circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a voltage source in series with a resistor
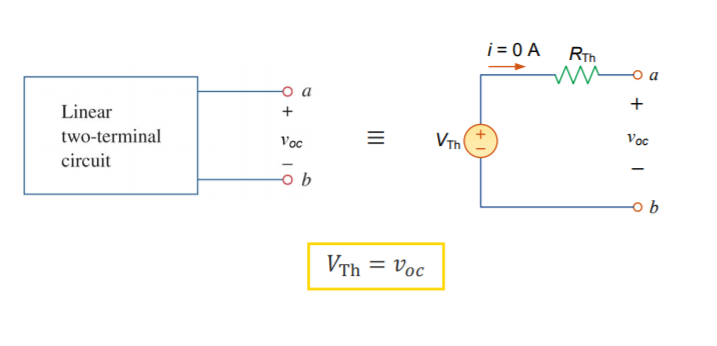
The voltage source's value is called the Thevenin voltage , and is equal to the open-circuit
voltage at the terminals![]()
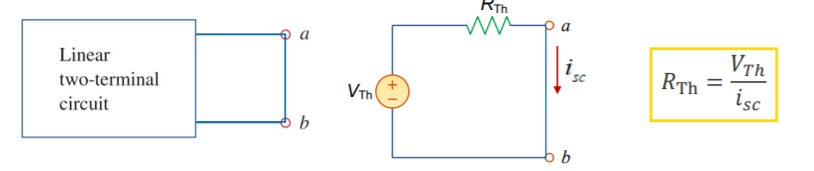
Thevenin resistance is equal to the ratio of the open-circuit
voltage to the source-circuit current at the terminal pair.![]()
Alternatively, can be calculated as the input resistance
measured at the terminals when all independent sources are turned off (method
cannot be used for dependent sources)![]()
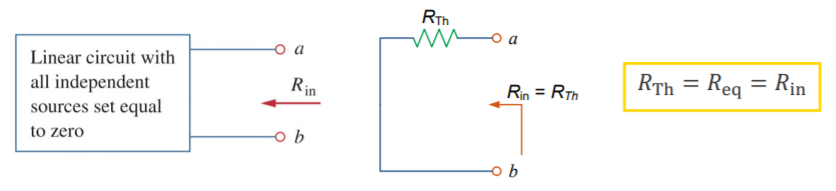
It is a powerful technique in circuit analysis with variable loads
It allows us to simplify a large linear circuit
The equivalent circuit behaves externally exactly the same way as the original circuit
The current through the load (or load current ) and the voltage across the load (load
voltage ) is obtained using a simple voltage
division, or KVL/KCL![]()