Norton's Theorem
Monday, 20 August 2018
12:58 PM
Norton's Theorem is the dual form of Thevenin's theorem
It provides a similar technique to simplify the analysis by replacing a linear circuit with an equivalent one, known as Norton's equivalent circuit
Norton's Theorem - A linear two-terminal circuit can be
replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a current source in parallel with a resistor ![]()
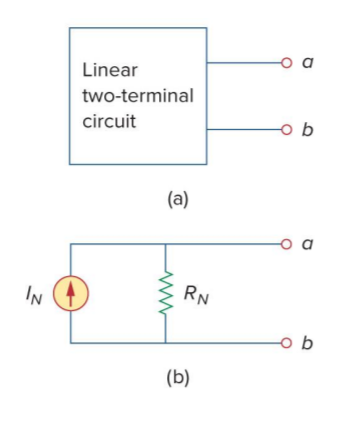
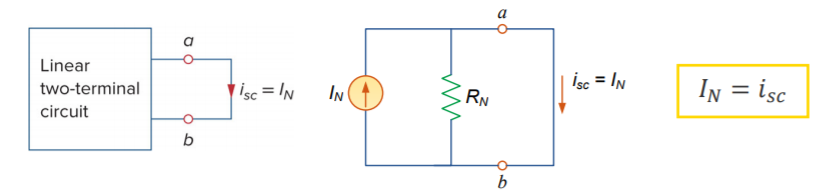
The current source's value, known as the Norton current , is equal to the short-circuit current
at the terminals.![]()
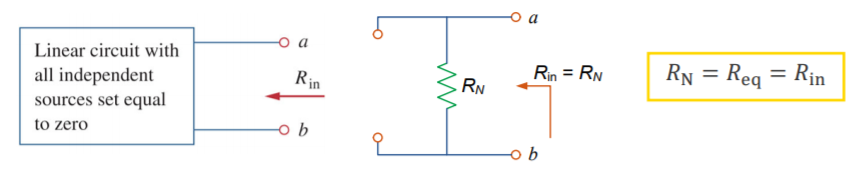
The Norton resistance is the same as the Thevenin resistance , which is the input resistance measured
at the terminals when all independent sources are turned off.![]()