Questions How-To
Contents
Circuit Switching
Consider a circuit-switched network with N=100 users where each user is independently active with probability p=0.2 and when active, sends data at a rate of R=1Mbps.
How much capacity must the network be provisioned with to guarantee service to all users?
There are 100 users, and any given moment it is possible for all users to to be using the network at the same time. Therefore if each user requires a 1 Mbps rate, then 100 * 1 Mbps => 100 Mbps capacity (plus a bit more).
Ignore any statistical information
Statistical Multiplexing
Consider a packet-switched network with N=100 users where each user is independently active with probability p=0.2 and when active, sends data at a rate of R=1Mbps.
What is the expected aggregate traffic sent by the users?
100 users * 0.2 * 1 Mbps == 20 Mbps
Delays
Consider a network connecting hosts A and B through two routers R1 and R2 like this:
A——-R1———-R2———B.
Does the queuing delay at R1 for a packet from A to B depend on the length of the link R1-R2?
No it doesn’t!
Transport
Pick the true statement
A. TCP provides reliability and guarantees a minimum bandwidth
B. TCP provides reliability while UDP provides bandwidth guarantees
C. TCP provides reliability while UDP does not
D. Neither TCP nor UDP provides reliability
HTTP
Non-Persistent HTTP (without parallelism)
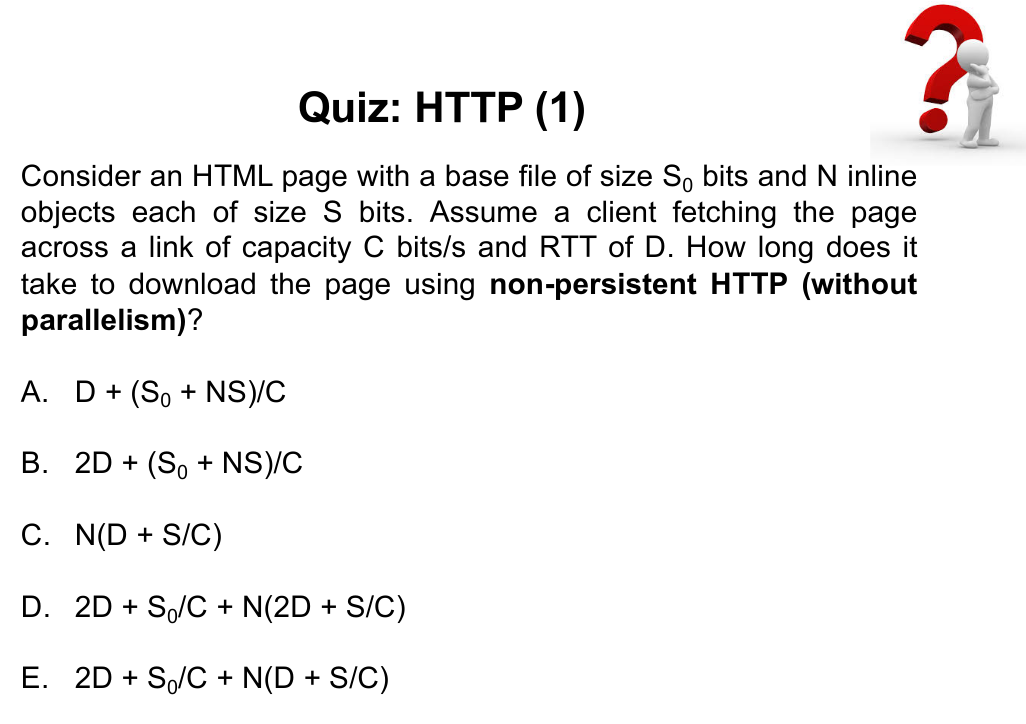
To fetch the base file: Initiate the connection (1 RTT) + Request for the file (1 RTT) + Get the data (S0 / C) = 2RTT + S0/C
To fetch the N objects: N * (Initiate the connection (1 RTT) + Request for the file (1 RTT) + Get the data (S / C)) = N(2RTT + S/C)
In total: 2RTT + S0/C + N(2RTT + S/C)
Answer: D
Persistent HTTP (without parallelism nor pipelining)

To fetch the base file: Initiate the connection (1 RTT) + Request for the file (1 RTT) + Get the data (S0 / C) = 2RTT + S0/C
To fetch the N objects: N * (Request for the file (1RTT) + Get the data (S / C)) = N(RTT + S/C)
In total: 2RTT + S0/C + N(RTT + S/C)
Answer: E
Persistent HTTP (with pipelining)

To fetch the base file: Initiate the connection (1 RTT) + Request for the file (1 RTT) + Get the data (S0 / C) = 2RTT + S0/C
To fetch the N objects: Request for the file (1RTT) + N * (Get the data (S / C)) = RTT + N(S/C)
In total: 2RTT + S0/C + RTT + N(S/C)
Answer: D
UDP

Answer: A
The server uses only one socket to receive, and send messages to each client
TCP

Answer: E
There is an extra socket that is used as a welcoming socket.
TCP Sockets

Answer: A
Each socket uses the same server-side port
TCP Sequence Number

Answer: C
TCP Sequence Number 2

Answer: A
TCP Timeout

Answer: D
RDT

Answer: D
Checksums, ACKs, Sequence Number

Answer: B
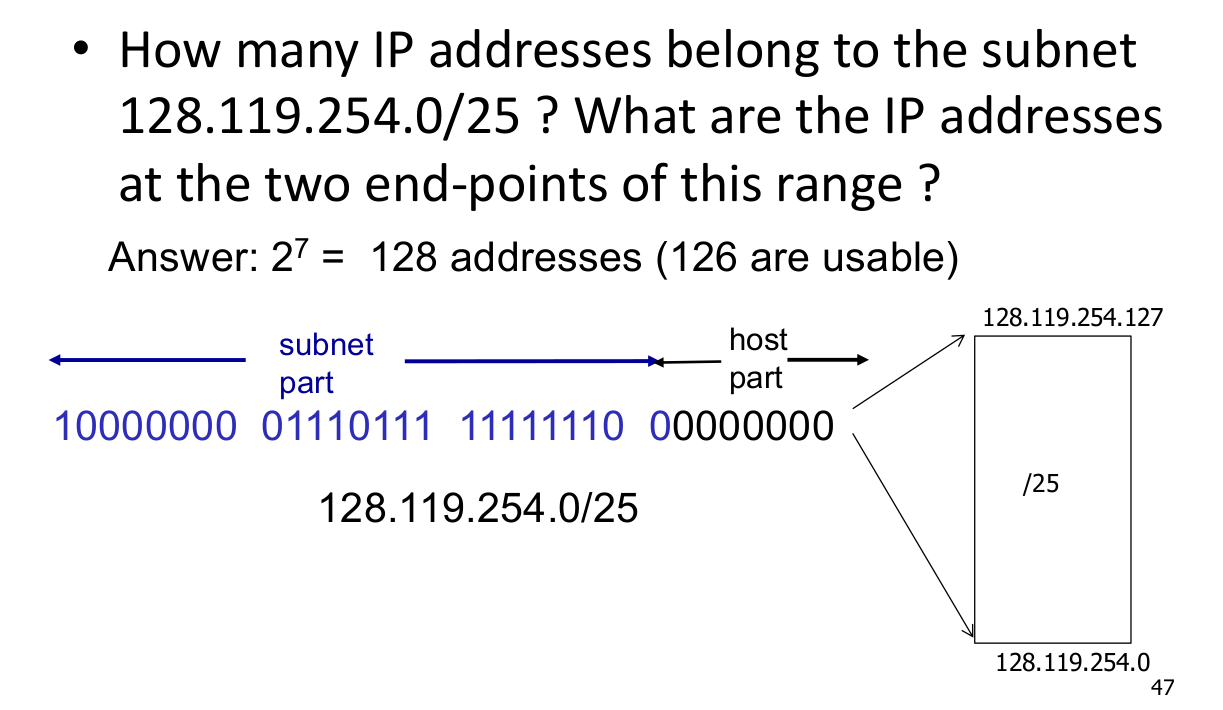
IP Subnets


Look at the host bits, and see the maximum number those bits can form (ie 2^n).
Remember, two of these address will be used by the network address and broadcast address, so there are 2^n - 2 usable addresses





Error Detection and Correction

Answer: C