Processes and Threads
Contents
A processor can only run one thing at a time. This include the OS itself.
When an application is running, the operating system itself is paused. However this does not feel apparent as regular interrupts (i.e. timers, interrupts) give control back to the OS.
- A process / task / job is the execution of an individual program. It owns the allocated resources
- A thread is a unit of execution which belongs to a process. They can be traced (List of executed instructions)
Structure

PID 8498 is the main process.
PIDs 8499 and 8500 are the threads
Process Model
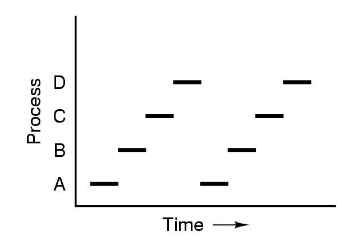
| One Program Counter | Four Program Counter | Process-Time Diagram |
|---|---|---|
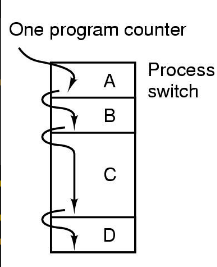 | 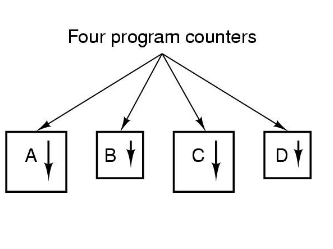 |  |
Uniprocessor -> Only one program can be active at any time
- One Process One Thread - e.g. MS-DOS
- One Process Multiple Threads - e.g. OS/161
- Multiple Processes One Thread - e.g. Traditional UNIX
- Multiple Processes Multiple Threads - i.e. Current major operating systems
Process Creation
Foreground - Interactive Background - Services / Daemons
Process Control Block
The PCB is a structure which holds the information related to a process.
For example its PID, signals, registers, program counter, stack pointer, state, priority, working directory, file descriptors, etc...
The process table is an array (of sorts) of PCBs.
Three State Process Model
Running, Blocked, Ready
Running: Currently running
Ready: Ready to run
Blocked: Busy (waiting for a syscall to be fulfilled)
--
- Running->Ready happens on a yield / end of time slice
- Running->Blocked happens when a process is waiting for input (file, network), timer (alarm), resource
Scheduler / Dispatcher
- Efficiently decides which process should run next (Queue)
- A queue is also used to decide the next blocked process to check.
- Event types (and consequently their respective event queue) can be created dynamically.
--
Thread Model
Is it better for multiple processes, or multiple threads?
Threads > Processes!??!?!
Related Metadata
- Address space
- Global variables
- Open files
- Child processes
- Pending alarms
- Signals
- Signal Handlers
Accounting information
Program Counter
Registers
Stack
State